As a parent, you may wonder what motivates your child to do things. Why do they sometimes seem eager to learn and explore, and other times seem bored and lazy? Why do they sometimes choose to do things that are good for them, and other times choose to do things that are harmful or risky? How can you help your child develop healthy motivation that will guide them to achieve their goals and fulfill their potential?
What is Motivation?
Motivation is the force that drives us to act. It is what makes us want to do something, and what keeps us going until we finish it. Motivation can come from different sources, such as our basic needs, our emotions, our thoughts, our values, our interests, or our social influences.
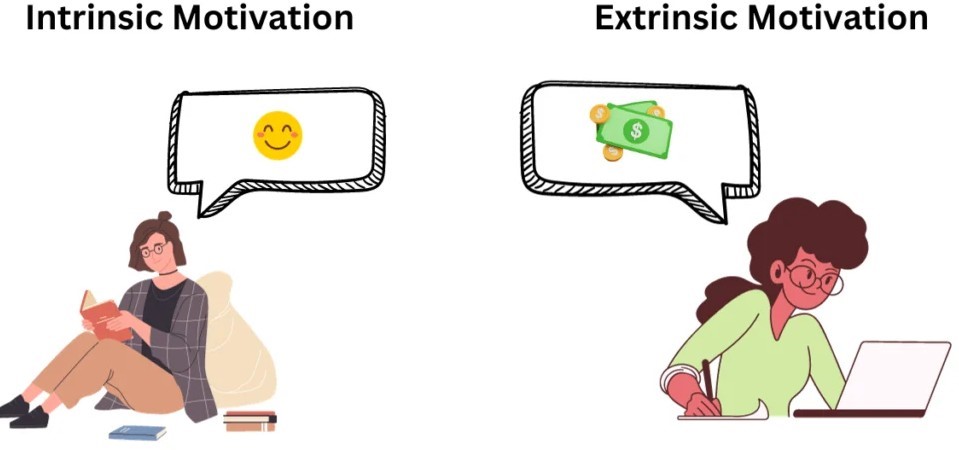
There are two main types of motivation: intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic motivation is when we do something because we enjoy it, find it interesting, or feel satisfied by it. Extrinsic motivation is when we do something because we expect a reward, avoid a punishment, or meet a requirement.
Some of the effects of alcohol on the brain are:
Motivation is the force that drives us to act. It is what makes us want to do something, and what keeps us going until we finish it. Motivation can come from different sources, such as our basic needs, our emotions, our thoughts, our values, our interests, or our social influences.
The two types of motivation
There are two main types of motivation: intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic motivation is when we do something because we enjoy it, find it interesting, or feel satisfied by it. Extrinsic motivation is when we do something because we expect a reward, avoid a punishment, or meet a requirement.
Both types of motivation can be useful, depending on the situation. For example, intrinsic motivation can help us pursue our passions and hobbies, while extrinsic motivation can help us complete our chores and duties. However, research has shown that intrinsic motivation is generally more beneficial for our well- being, learning, and performance.
Intrinsic motivation can also foster creativity, curiosity, and self- determination.
How Does Motivation Relate to Emotion and Cognition?
Motivation is closely related to both emotion and cognition. Emotion is the feeling that accompanies our motivation, such as joy, excitement, fear, or anger. Cognition is the thinking that influences our motivation, such as beliefs, goals, plans, or strategies.
Emotion and cognition can work together or against each other when it comes to motivation. For example, if we are motivated to do something that makes us happy and aligns with our values, our emotion and cognition are in harmony. But if we are motivated to do something that makes us anxious and contradicts our beliefs, our emotions and cognition are in conflict.
Sometimes, emotion can be a stronger motivator than cognition. We may do things that are emotionally pleasurable but logically unwise, such as having one more piece of chocolate brownie after having a few. This is because emotion can trigger our basic drives, such as hunger, thirst, fear, or reproduction, which are essential for our survival and evolution. These drives can override our rational thinking and make us act impulsively or instinctively.
However, emotion can also be a positive motivator, especially when it is linked to our intrinsic motivation. When we do something that we love, we feel positive emotions, such as joy, pride, or gratitude. These emotions can reinforce our motivation and make us want to do more of the same. Positive emotions can also broaden our perspective and enhance our creativity, learning, and problem-solving.
How to Help Your Child Develop Healthy Motivation :
As a parent, you can help your child develop healthy motivation by following these tips:
Encourage your child’s intrinsic motivation:
Help your child discover and pursue their interests, passions, and strengths. Provide them with opportunities to explore, learn, and create. Praise them for their effort, progress, and achievements. Avoid using rewards, punishments, or pressure to motivate them, as these can undermine their intrinsic motivation and make them dependent on external factors
Support your child’s emotional regulation :
Teach your child how to identify, express, and cope with their emotions. Help them understand how their emotions affect their motivation and behavior. Model positive ways to deal with stress, frustration, or disappointment. Help them find healthy outlets for their emotions, such as physical activity, music, or art.
Foster your child’s cognitive skills :
Help your child develop their thinking and reasoning abilities. Teach them how to set realistic and attainable goals, plan and organize their tasks, monitor and evaluate their performance, and adjust their strategies as needed. Help them learn from their mistakes and failures, and see them as opportunities for growth. Encourage them to seek feedback and guidance from others.
Nurture your child’s autonomy and self-determination :
Respect your child’s choices and preferences, and involve them in decision-making. Allow them to have some control and responsibility over their own actions and outcomes. Provide them with clear and consistent expectations and boundaries, and explain the reasons behind them. Support them in overcoming challenges and obstacles, but avoid doing everything for them.
Create a positive and supportive environment :
Provide your child with a safe and comfortable space to do their activities. Ensure that they have enough time, resources, and materials to complete their tasks. Minimize distractions and interruptions that may interfere with their concentration and motivation. Show interest and enthusiasm in what they do, and celebrate their successes and efforts.
Understanding and nurturing your child’s motivation is crucial for their well-being and development. Motivation, influenced by both emotion and cognition, plays a pivotal role in their choices and behaviors. Differentiating between intrinsic and extrinsic motivation, focus on fostering intrinsic motivation for long-term success
As a parent, support your child’s interests, teach emotional regulation, enhance cognitive skills, nurture autonomy, and create a positive environment. These actions empower your child to navigate challenges, set goals, and explore their potential, laying the groundwork for a motivated and resilient approach to life.
Happy Parenting!
